Attaching a second belay system to the ZIGZAG
The ZIGZAG’s auxiliary attachment point enables a second belay system or a lanyard to be attached, without limiting the arborist’s mobility.
Warnings
- Carefully read the Instructions for Use used in this technical advice before consulting the advice itself. You must have already read and understood the information in the Instructions for Use to be able to understand this supplementary information.
- Mastering these techniques requires specific training. Work with a professional to confirm your ability to perform these techniques safely and independently before attempting them unsupervised.
- We provide examples of techniques related to your activity. There may be others that we do not describe here.
Note: in this document the name ZIGZAG means either the ZIGZAG or ZIGZAG PLUS models.
When the arborist has two systems connected to the attachment bridge of their harness, they have less freedom to turn while moving or cutting. If they do not pay attention, the two systems become crossed.
With the second system connected directly to the first ZIGZAG, especially with the ZIGZAG PLUS swivel, full mobility is retained and the arborist can easily turn without crossing their ropes.
Two systems on the same bridge
- Less mobility of the systems on the harness bridge, when the arborist has to turn around to cut a limb for example.
- Crossing systems is possible when moving in the tree.
- Possibility of interference and friction between the two systems.
Two systems on two bridges
- The two systems are completely independent.
- Crossing systems is possible when moving in the tree.
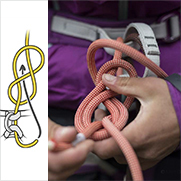
Second system connected to the first ZIGZAG
- Complete freedom to turn around in all situations.
- Less crossing of systems when moving in the tree.
- The two systems are not completely independent: the arborist is attached to a single connector.